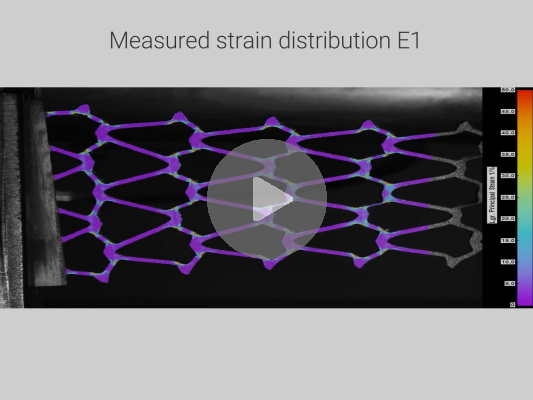
Full field strain measurement with maximal spatial resolutionThe Istra4D measurement software used in the Q400 DIC system uses a special algorithm to achieve maximum possible spatial resolution. This example shows that the spatial resolution of the strain field is significantly improved by an appropriate image evaluation algorithm. In combination with a high camera resolution, the Q400 system is unsurpassed in terms of spatial resolution. Why is a high spatial resolution needed for strain measurement?Localization of strain peaks: High spatial resolution enables strain peaks or concentrations to be precisely located. This is important to identify areas of increased strain that may indicate critical stresses or potential weak points. Detection of local deformations: Thanks to a high spatial resolution, the DIC method can also accurately detect local deformations. This is particularly important when examining materials or structures that are not homogeneous or have local deformations, such as fiber-reinforced plastics or composite materials. Detailed analysis of structural components: When characterizing complex structural components, high spatial resolution is required to accurately measure local strains or deformations in areas such as welds, edges or corners. This allows for detailed analysis and assessment of structural integrity. Improved accuracy: High spatial resolution results in improved accuracy of strain measurements because smaller areas of the object or structure can be analyzed. This helps obtain more precise results and improves the reliability of measurements. Detection of local material anomalies: By measuring strains with high spatial resolution, local material anomalies such as cracks, delaminations or other defects can be more easily detected. This is important for quality assurance and error analysis in various applications. Overall, a high spatial resolution of strain measurement is important in the DIC method in order to enable a detailed analysis of strains and deformations in materials and structures. This contributes to improving the understanding of material and structural mechanics and supports the development and optimization of products and processes. |